Biogas
for Cooking, Lighting & Micro-Electricity
Imagine a rural school kitchen with gas stoves and enough gas to cook a daily meal for all pupils without any need to
source, transport and pay for cooking gas? No toxic smokes, quick and healthy cooking. In the evenings, the school and
its library are a bright centre for adult learning and a popular meeting place, enlightened by several gas lamps which also
shed light on the main village road. Besides, the hygiene education of the pupils is high because everyone is proud to
produce their own lighting and cooking energy, naturally and freely available... Impossible? Not at all.
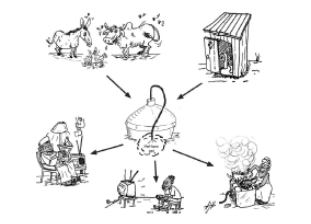
Biogas is produced through the digestion of organic matter by anaerobic bacteria in an oxygen-free surrounding. These
bacteria are producing methane gas as a by-product of their digestion process. Unlike in a compost heap, where the
decomposition is shared by aerobic and anaerobic bacteria and the methane gas is released into the atmosphere, the gas
can be collected in a closed biogas digester.



1 - Biogas Digester Types
2 - Cooking with Biogas
3 - Lighting with Biogas
4 - Electricity Generation
with Biogas
5 - Pros & Cons of Biogas
7 - Biogas Best Practices











